Session limits
Session limits define how many concurrent sessions a user can open, and of which type.
Useful resources
Restrict the number of concurrent sessions a user can have.
Completely block certain session types (e.g., forbid VPN by setting the limit to 0).
Apply different limits depending on session type (e.g., 2 workstations + 1 VPN).
Reduce risks linked to multiple forgotten or unattended sessions.
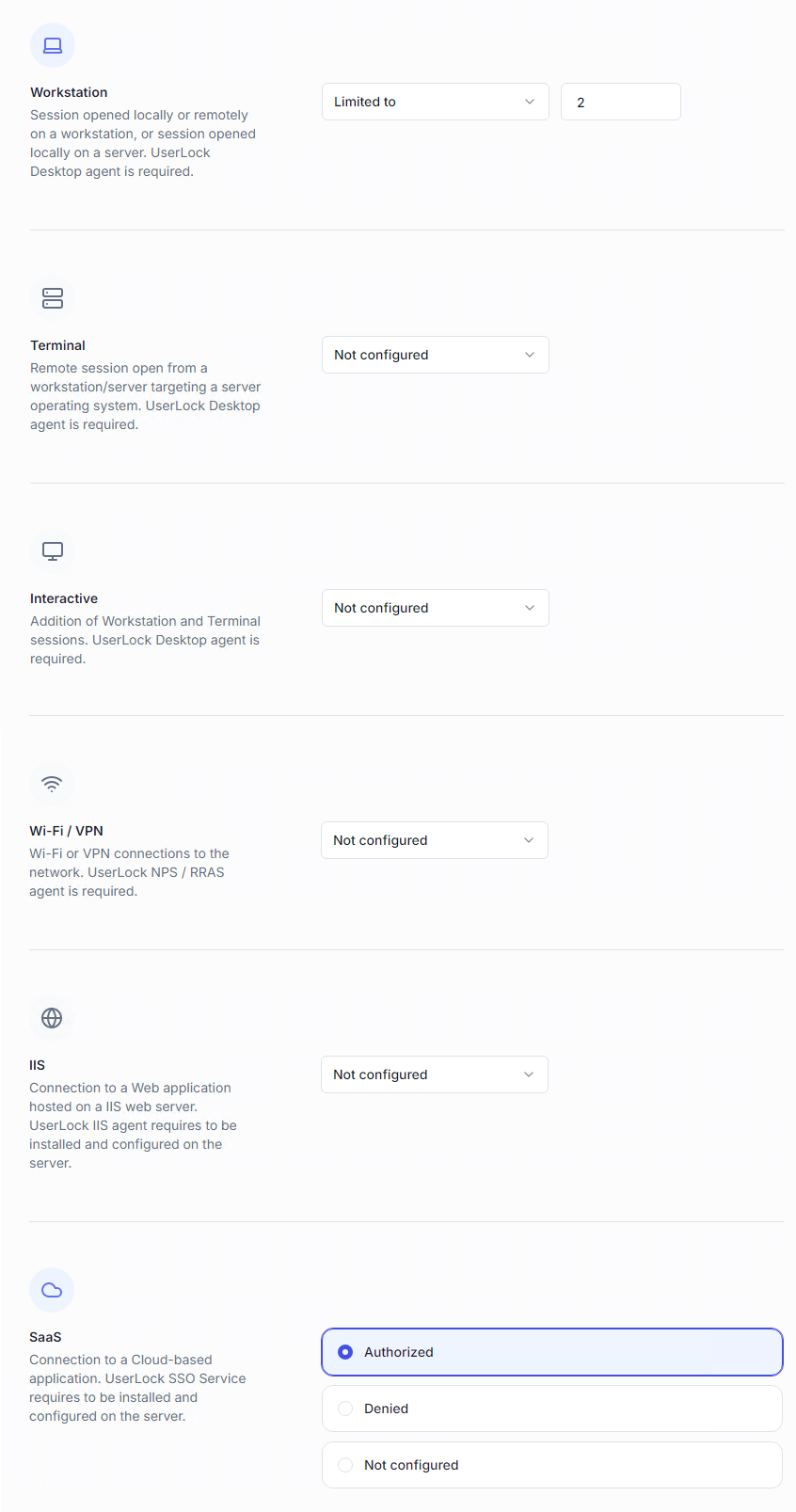
For each session type (Workstation, Terminal, Interactive, Wi-Fi/VPN, IIS, SaaS), you can set:
Not configured → no limit, unless inherited from another policy.
Unlimited → no restriction.
Limited to → maximum number of sessions allowed (0 = forbidden).
Interactive sessions = combined total of Workstation + Terminal sessions.
SaaS does not use numeric limits: you simply choose Authorized or Denied.
Group limits: when applied to a group or OU, the limit applies collectively to all members (total sessions across the group).
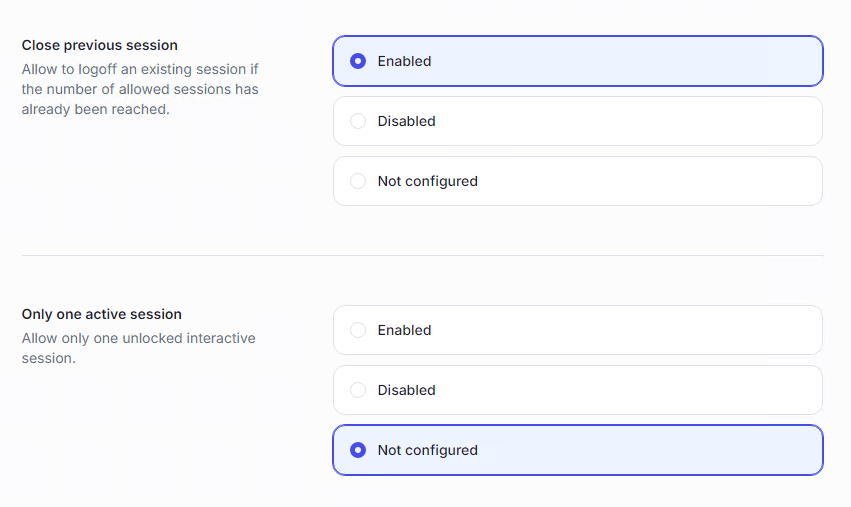
Advanced options:
Close previous session → allows a user to remotely log off an existing session to open a new one. Warning: forced logoff means unsaved work is lost.
Only one active session → the user can keep only one interactive session active at a time. Any other will be automatically locked/disconnected.
Custom session limits → define a total limit across multiple selected session types (e.g., max 5 sessions including workstation + terminal + VPN).
Note
This policy can be combined with Initial access points for stronger control.
Example: limit to 2 initial access points + 5 total sessions → the user can connect from two machines, but cannot exceed five sessions in total.
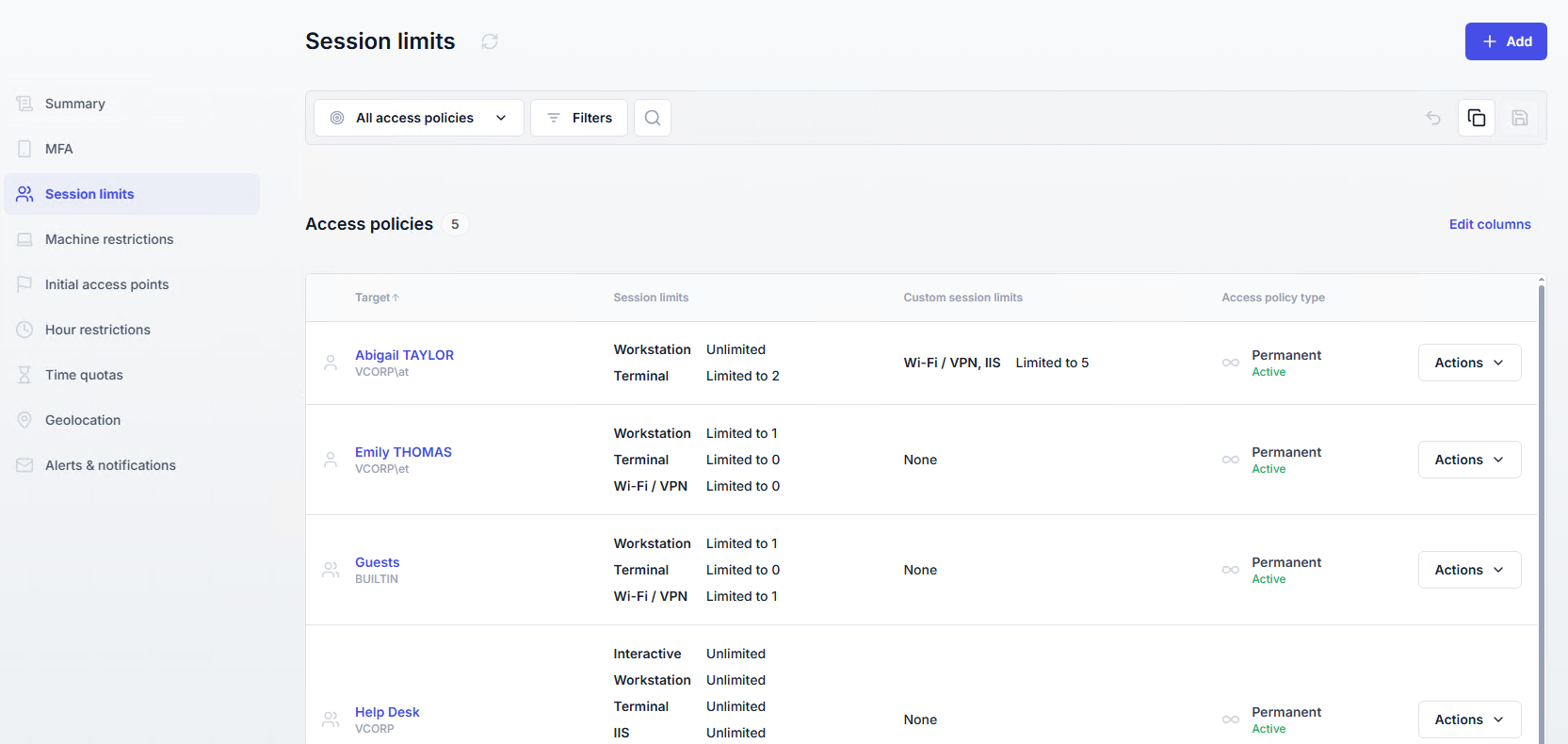
A list of all session limit policies is available in the Access Policies section, under the Session limits page.