Configure AWS for UserLock SSO
Connect AWS logins to UserLock Single Sign-On (SSO) to centralize authentication, enforce corporate access policies, and simplify user access to AWS resources.
This guide explains how to integrate Amazon Web Services (AWS) with UserLock Single Sign-On (SSO) using the SAML 2.0 protocol.
Once configured, AWS logins are authenticated by UserLock against Active Directory. This provides a seamless sign-in experience and allows administrators to enforce UserLock access policies (MFA, time, machine, or location restrictions) on AWS sessions.
🚩️ Before starting:
You need an AWS Organization account and a test user account available in AWS.
UserLock SSO must already be installed and configured.
Go to UserLock console▸ ⚙️ Server Settings▸ Single Sign-On
Click on Download ▸ Metadata file.
Open the AWS console.
Enable AWS SSO.
In Settings, change the Identity Source to External Identity Provider.
Under Identity Provider metadata, upload the UserLock metadata file previously download.
In the AWS accounts section, select your AWS account and click Assign Users.
Add the test user account.
Launch the User portal URL (available in AWS SSO Settings) to verify that the integration works.
Note
💡 Best practice: start with a single test user before rolling out to production.
In the UserLock console, go to ⚙️ Server settings ▸ SSO.
Click on the AWS row.
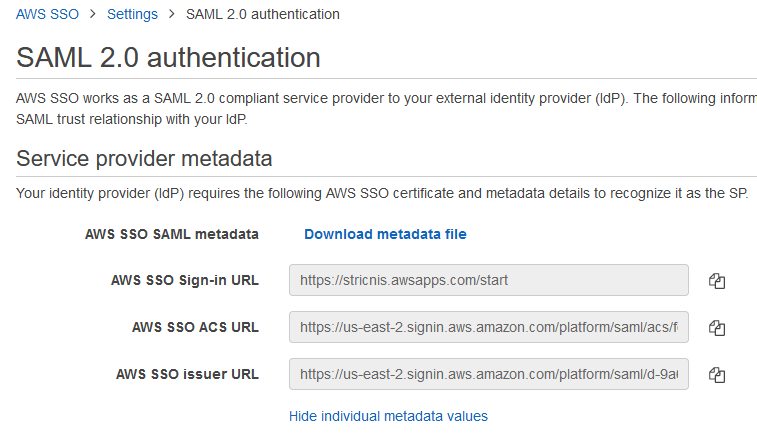
Fill in the fields with information from the AWS SSO console:
Settings
Values
Email domain
The domain used by your AWS users (e.g. contoso.com).
Issuer
Copy / paste AWS SSO issuer URL from the AWS SSO console
ACS URL
Copy / paste AWS SSO ACS URL from the AWS SSO console
When the SAML certificate expires in UserLock, you must update AWS with the new metadata.
In the AWS SSO console, go to Settings.
In Identity Source, click Change.
Enter the new UserLock SSO metadata URL in the IdP SAML metadata field:
https://<your_ul_sso_url>/metadata
For common issues, see Troubleshooting SSO.
If the problem persists, please contact IS Decisions Support.
You can extend the security of SSO sessions by applying UserLock access policies in addition to authentication.
Apply MFA on SaaS connections to require stronger authentication.
Hour restrictions: define when users are allowed to connect.
Geolocation rules: enforce access policies based on user location.
Session limits: allow or deny SaaS logins entirely for specific users.