Enforce firewall requirements
Learn how to configure Windows Firewall to allow secure communication between the UserLock server and protected computers. This guide covers both manual configuration and centralized deployment through Group Policy.
📘 Useful resource
For the full list of protocols, ports, and communication flows used by UserLock, see Communication and required protocols.
UserLock requires specific Windows Firewall rules to ensure reliable communication between the UserLock server and protected workstations or terminal servers.
You can configure these rules:
Individually, on each machine (useful for tests or small setups)
Centrally, through Group Policy Objects (GPOs) (recommended for large environments)
Important
Before proceeding, ensure that the UserLock service impersonation account has administrative rights on all protected computers.
File and Printer Sharing rules allow the UserLock server to communicate with workstations and deploy desktop agents.
Open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
In the left pane, select Inbound Rules, then click New Rule...
Choose Predefined → File and Printer Sharing → Next.
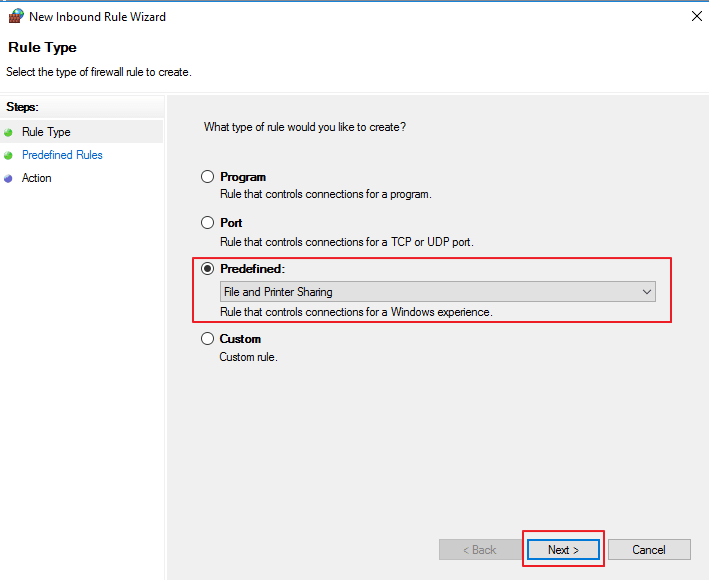
Select and enable the following rules:
File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request – ICMPv4-In)
File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request – ICMPv6-In)
File and Printer Sharing (SMB-In)
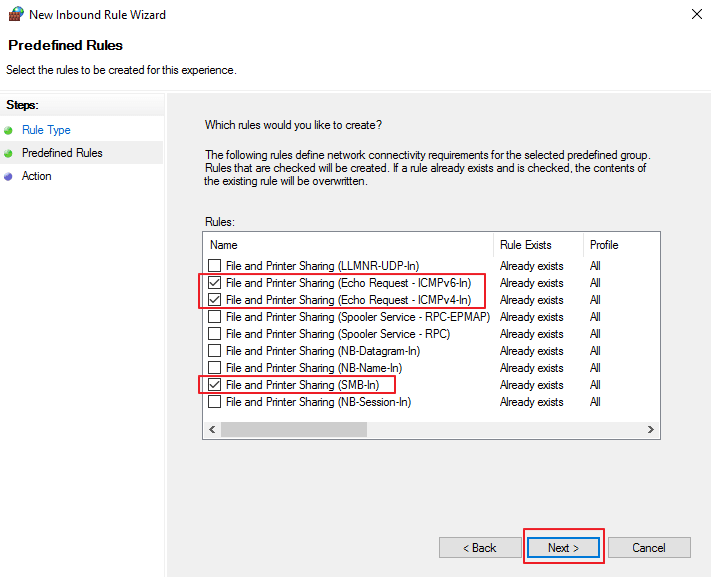
Click Finish.
)
For enhanced security, limit File and Printer Sharing and Remote Registry access so that communication occurs only between the UserLock server and protected computers.
Open the Properties of each previously created rule.
Go to the Scope tab.
Define allowed IP addresses as follows:
Local IP address: Add the IP(s) of the UserLock server(s).
Remote IP address: Add the subnet or IP range of the protected machines.
)
Local IP address: Add the subnet or IP range of the workstations.
Remote IP address: Add the IP(s) of the UserLock server(s).
)
Example
If all workstations use 10.3.1.1/255, set that as the IP range on both sides.
For larger environments, deploy firewall rules through Group Policy to ensure consistency across all machines.
You’ll need two separate GPOs:
One for UserLock server(s)
One for protected machines
Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
Create or edit a GPO for each scope (UserLock server or workstations).
Navigate to:
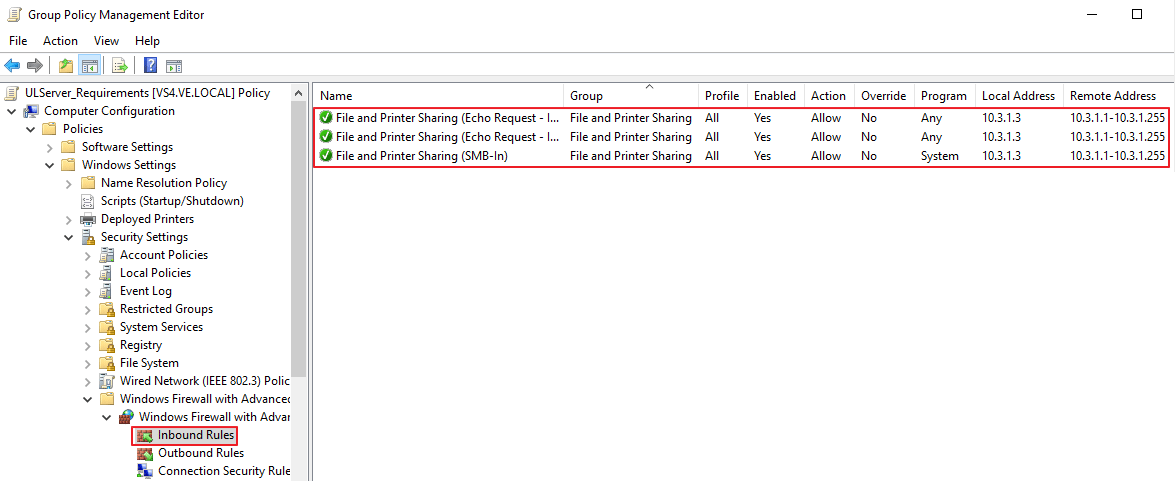
Computer Configuration → Policies → Windows Settings → Security Settings → Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security → Inbound RulesRight-click Inbound Rules → New Rule...
Follow the wizard to recreate all required rules (File and Printer Sharing, Remote Registry, etc.) as described above.
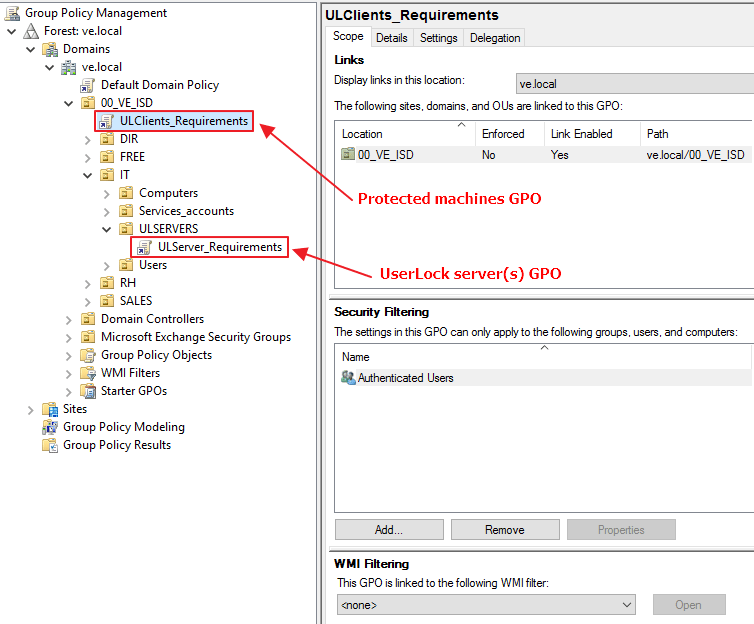
Link the GPO to the Organizational Unit (OU) containing your UserLock server(s).
Configure inbound rules to allow connections from the IP range of the protected machines.
Link the GPO to the OU containing your protected computers.
Configure inbound rules to allow connections from the UserLock server IP(s).
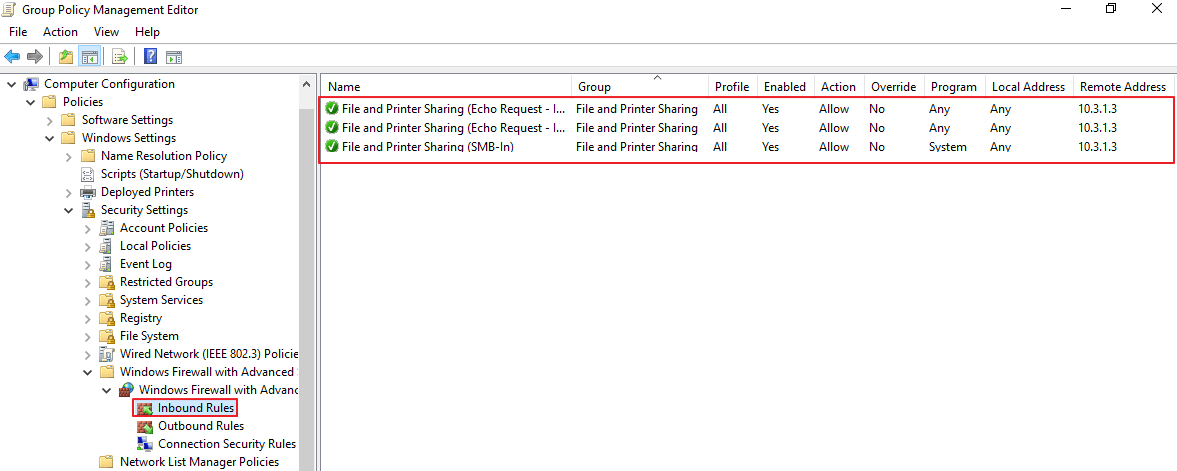
Document all IP ranges to prevent accidental exposure.
Verify that GPOs are applied correctly using
gpresult /rorrsop.msc.Test connectivity between the UserLock server and a sample workstation using:
ping(ICMP) for network reachability\\ServerName(SMB) for file sharing validation
💡️ Once the firewall rules are configured, you can verify that all required communications are working correctly by following the guide Check services and network protocols requirements.
)
)
)