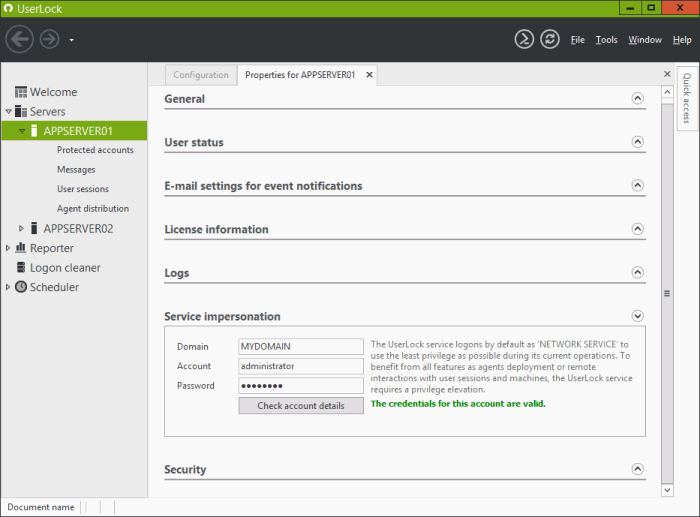
Service impersonation
When installing the application, the UserLock service is configured to logon by default as the 'Network Service' account to use the least privilege as possible during its current operations. That's why, during the UserLock installation, the 'Configuration wizard' requests an impersonation account which will be used instead of the 'Network Service' for all operations requiring higher privileges, i.e. administrative rights on target machines, such as:
- The deployment of all agent types.
- The system operations performed when applying user access control rules i.e. lock sessions, logoff sessions.
- The automatic logoff performed by the option closing disallowed sessions.
- The system operations performed on demand i.e. lock sessions, logoff sessions, shutdown machines, restart machines.
- The synchronizations between the Primary server and the Backup server.
- The connection to the database when using the 'Windows authentication' mode.
This section displays the credentials entered during the corresponding 'Configuration wizard' step and allows you to edit/change them if necessary.
Please note:
- As the impersonation account is the credential used when the UserLock service connects to the database in 'Windows authentication' mode to save all session events, this account needs to be granted permission to connect to the database server and to manage the UserLock database.
- No modifications will be made to your Active Directory or its schema.
- The impersonation account is used by the UserLock service only. The UserLock Desktop Agent runs as a local SYSTEM account on the associated computer.
- The account "<domain>\<UserLock server name>$" must have authorized read access to user and computer data in Active Directory.
- The impersonation account must have permission to log on as a service. Before changing this setting, log in to the UserLock server, open "Local Security Policy" ("secpol.msc"), "Local Policies", "User Rights Assignment", check that the target account is in the "Log on as a service" list and it is not in the "Deny logon as a service" list.