7 Best Practices for Configuring FileAudit
Here are our recommendations on what to do when first configuring FileAudit.
-
Avoid configuring paths containing system files
During the audit configuration, avoid configuring paths containing system files, as the operative system triggers many of its own set of events on these files.
(Specific example of system files include the files with .sys filename extension in MS-DOS. In Windows NT family, the system files are mainly under the folder C:\Windows\System32.)
-
Configure during off-peak hours for a large amount of data
When auditing a large amount of data (>1 TB), configure during off-peak hours, and if possible in batches.
The reason for this is FileAudit checks the inheritance configuration on first levels of sub folders to be sure that the NTFS settings will be correctly propagated and that the audit will be enabled on all subfolders and files. This can take some time depending on the amount of files and folders and the performance of the server.
-
Exclude common unwanted file events
To optimize your audit, it is best to exclude certain file events such as temporary documents and events generated with executables such as antiviruses or backups. Service accounts that can generate unwanted events should also be excluded.
Go to Settings => Scan Options, and enter the file types and executables that you do not wish to audit. See the screenshot below for the more common exclusions:
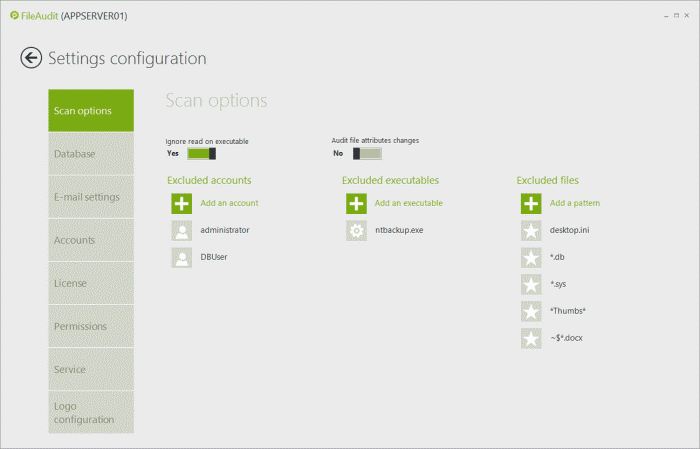
-
Alert on suspicious behavior
Three alerts can be easily configured, straight away. The sooner you detect inappropriate or suspicious access, the sooner you can stop it!
-
I. Set up a ‘single access alert’ for file extensions that can be generated from a ransomware, such as .cryptolocker. The screenshot below shows a list of common ransomware extensions.
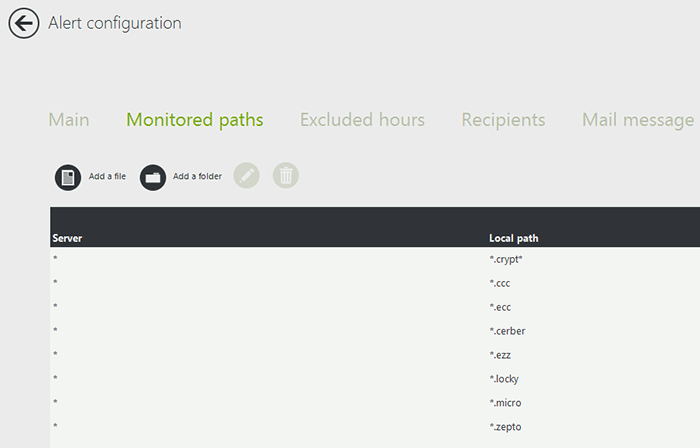
-
II. Create a ‘single access alert’ for any “denied” access type on your most sensitive files and folders.
-
III. Configure a ‘mass access alert’ for when any particular user performs a large number of access events in a short period of time.
Bulk File Copying: When a significant number of read accesses are performed during a short period of time, the probability is that the user has executed a copy/paste file operation.
Bulk File Deletion or Movement: When a significant number of deletions are performed during a short period of time, the user has either deleted or moved a number of files.
-
-
Configure a database that is adapted to your environment
When choosing a database, take into consideration the database size, number of events generated, and how long you would like to keep your data.
An access event audited by FileAudit consumes 0.5 KB of disk space when saved in the database. Knowing this you can easily estimate the evolution of the database size by multiplying this value by the average number of access (known or observed during the tests phase).
The software also has a built-in cleaner tool to schedule regular clean ups to avoid a saturated database.
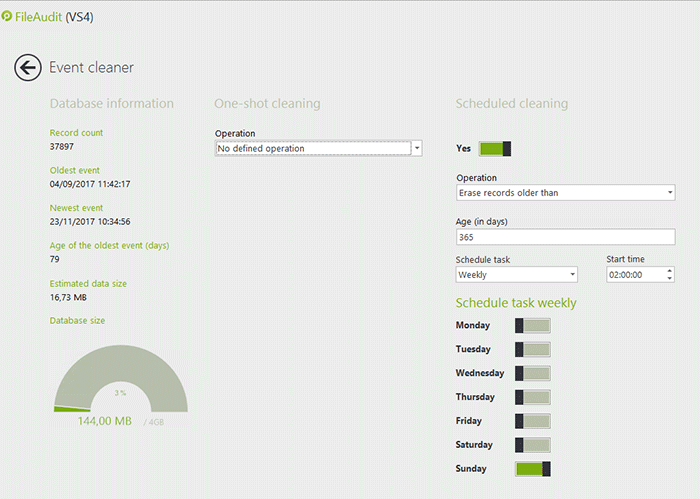
-
Activate email notifications for warning messages
Under Settings => Service, enable the email notifications feature to be alerted if there is an issue with the software. This allows you to troubleshoot as soon as the issue occurs, and to avoid losing any audited data.
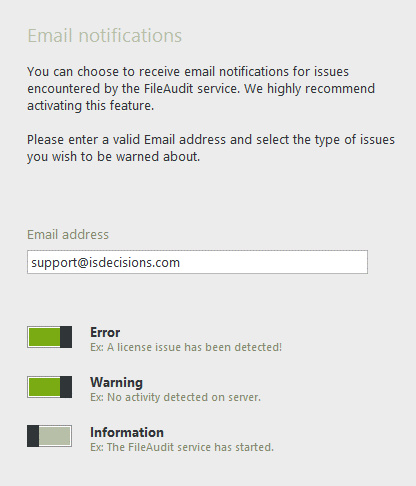
Now You: Have another tip? Feel free to share it with the team at IS Decisions.