Support CMMC compliance, protect sensitive data
UserLock and FileAudit support security requirements at the highest levels for CMMC 2.0.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a unified standard developed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). CMMC’s purpose is to enhance the cybersecurity posture of the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) and protect sensitive data. It sets forth a framework that contractors and subcontractors must follow to safeguard Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI).
The latest iteration of the DoD’s CMMC cybersecurity model is the CMMC 2.0 program. Starting November 10, 2025, the DoD will enforce CMMC 2.0 certification as a condition for awarding contracts.
CMMC 2.0 streamlines requirements, simplifying to three instead of five levels of cybersecurity. At each level, CMMC 2.0 also aligns requirements more closely with the familiar NIST cybersecurity standards, such as NIST 800-53 and NIST-800-171.
Overall, CMMC 2.0 puts a strong focus on access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) as essential to protecting sensitive data.
IS Decisions’ software UserLock and FileAudit directly address high-priority security control baselines across all levels in CMMC 2.0, including:
Identification and authentication (IA)
Access controls (AC)
Audit and accountability (AU)
System and information integrity (SI)
Talk to a product expert
Learn how UserLock and FileAudit can help your organization meet key CMMC 2.0 requirements.
IA.L1-3.5.2 Authentication: Authenticate (or verify) the identities of those users, processes, or devices, as a prerequisite to allowing access to organizational information systems.
IA.L2-3.5.3 Multifactor authentication: Use multifactor authentication for local and network access to privileged accounts and for network access to non-privileged accounts.
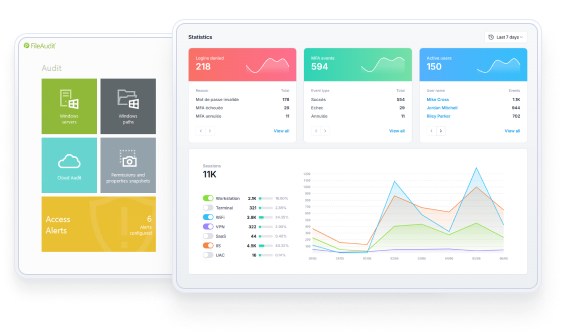
UserLock makes it easy to verify the identity of all Active Directory accounts, whether privileged or non-privileged, and secure access to your network with straightforward MFA for CMMC on Windows logon, RDP, RD Gateway, RemoteApp, VPN, VDI and SaaS connections.
There are two edit modes available for modifying the MFA settings. Make sure to read the documentation for the use case for each type of session to ensure users will receive an MFA prompt.
With UserLock, you can set MFA policies for:
All session types at once: By selecting this option, you can apply the same policy for all session types that are protected by UserLock.
Different sessions and connection types: With this option, you can apply granular policies across different connections and sessions.
Connection type: Choose to apply MFA to all connection types, only to remote or outside connections, or to none.
Session type: Apply different MFA policies for each session type.
Frequency: Choose how often to prompt for MFA, setting different rules for each session type.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
Here's how UserLock maps to key CMMC access control requirements.
AC.L1-3.1.1 Authorized access control: Limit information system access to authorized users, processes acting on behalf of authorized users, or devices (including other information systems).
AC.L1-3.1.2 Transaction & function control: Limit information system access to the types of transactions and functions that authorized users are permitted to execute.
AC.L2-3.1.7 Privileged functions: Prevent non-privileged users from executing privileged functions and capture the execution of such functions in audit logs.
AC.L2-3.1.5 Least privilege: Employ the principle of least privilege, including for specific security functions and privileged accounts.
Since UserLock integrates with your Active Directory, you can quickly set up access policies for AD users, groups, or organizational units (OUs). This helps you implement security policies in line with the principle of least privilege, ensuring users only have access to the information they need to do their job.
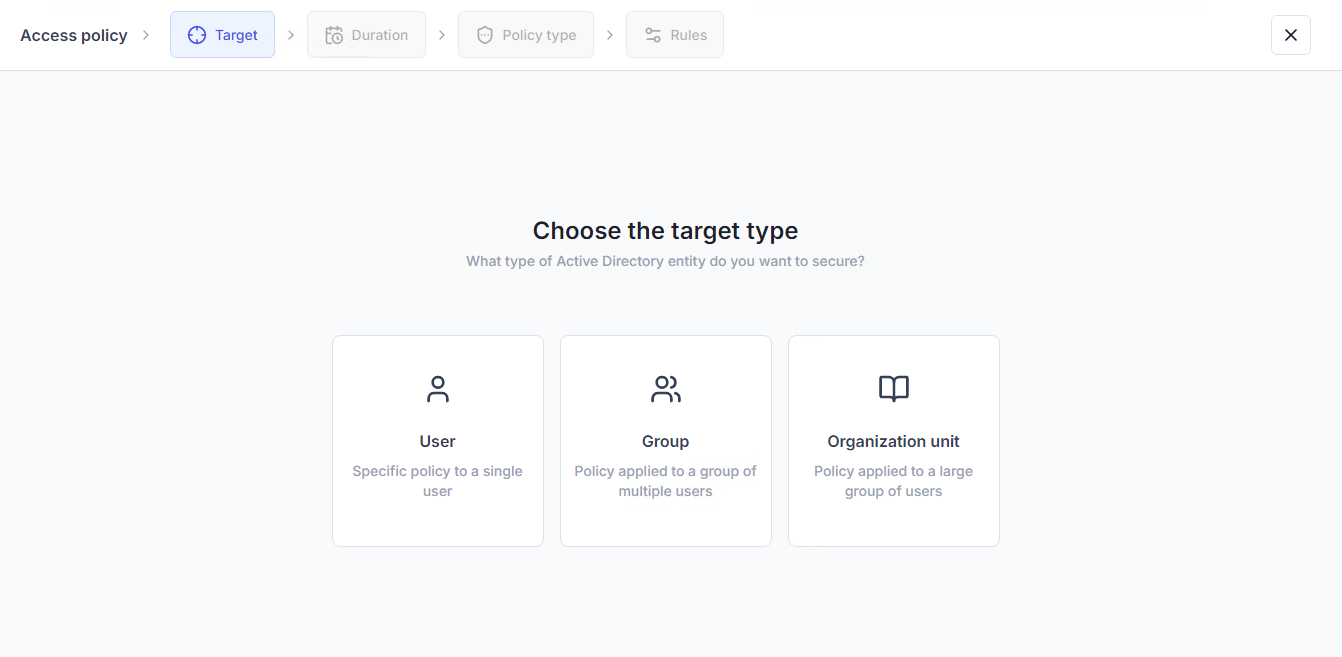
Then, you can set granular access controls to limit information system access to verified AD identities. For example, by combinging MFA with contextual access restrictions.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
Critical for CMMC 2.0, you can then prove you have set up and enforce strong access controls with UserLock reports. Thanks to a central audit across the whole network, you can log and report on all user connection events.
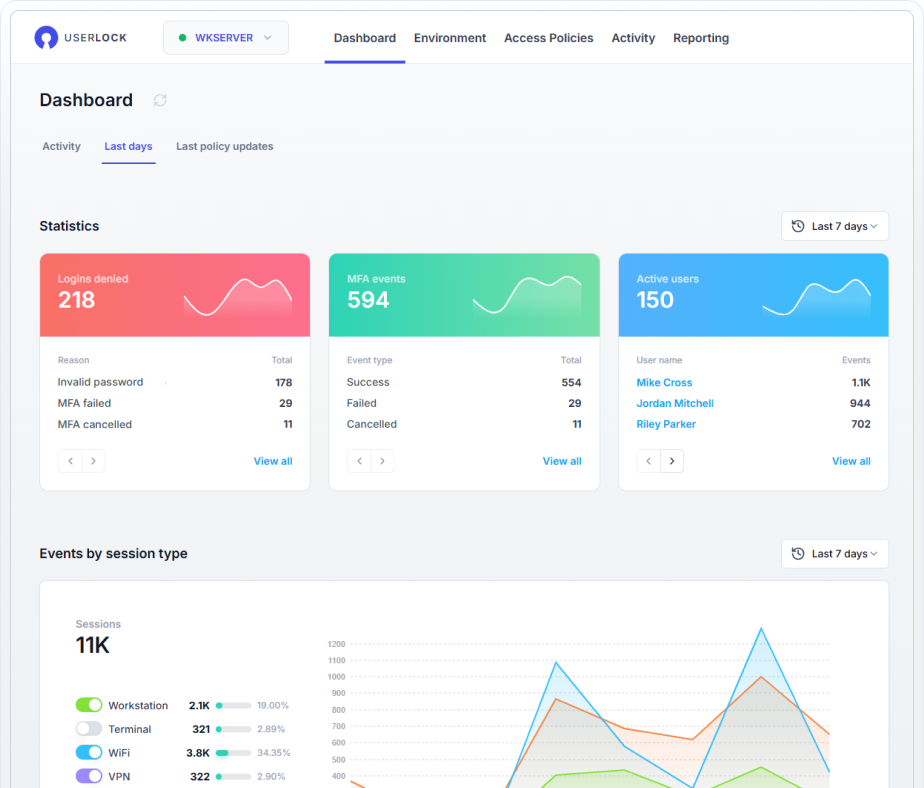
AC.L2-3.1.10 Session lock: Use session lock with pattern-hiding displays to prevent access and viewing of data after a period of inactivity.
AC.L2-3.1.8 Unsuccessful logon attempts: Limit unsuccessful logon attempts.
AC.L2-3.1.11 Session termination: Terminate (automatically) a user session after a defined condition.
Any logon attempts that don’t satisfy your login restrictions are automatically blocked.
Administrators also can review and immediately block any suspect access with one click.
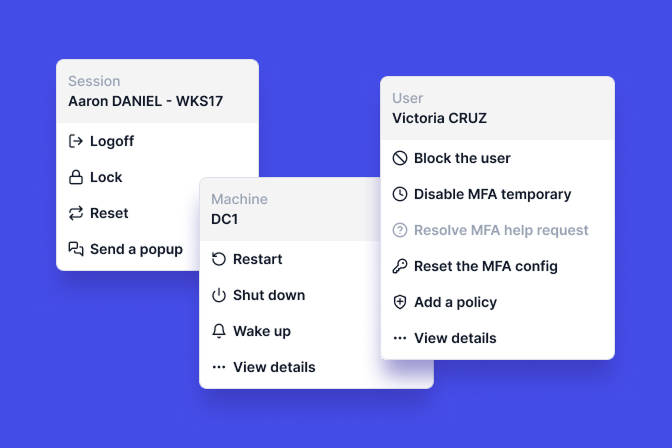
This denies all further logon attempts and closes any existing sessions.
They can also set an automatic forced logoff, on all locked or open machines, after a certain idle time. This includes remote desktop sessions opened by the domain user.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
AC.L2-3.1.12 Control remote access: Monitor and control remote access sessions.
UserLock also helps administrators manage and secure remote access for all users, without getting in employees’ way or creating more work for the IT department.
If your remote users aren’t connected to the corporate domain or don’t use a VPN, you can choose if and how to maintain policies in offline scenarios. This also applies if a remote user logs on without an internet connection.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
To easily monitor or report on remote sessions, you can filter the session history view to see all remote sessions, in real-time or by date.
Both UserLock and FileAudit support CMMC audit and accountability (AU) requirements.
AU.L2-3.3.1 System auditing: Create and retain system audit logs and records to the extent needed to enable the monitoring, analysis, investigation, and reporting of unlawful or unauthorized system activity.
AU.L2-3.3.2 User accountability: Ensure that the actions of individual system users can be uniquely traced to those users, so they can be held accountable for their actions.
UserLock monitors, records, and reports on every user access event and logon attempt to a Windows domain network.
In the UserLock dashboard, administrators can also access and easily filter through detailed and customizable reports to prove compliance and support forensic investigations.
And, you can also drill down to see individual user access event reports. This helps administrators trace user access at all times, and making users accountable for any activity — whether malicious or not.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
AU.L2-3.3.8 Audit protection: Protect audit information and audit logging tools from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion.
AU.L2-3.3.9 Audit management: Limit management of audit logging functionality to a subset of privileged users.
UserLock helps control administrator actions, with granular controls on permission rights for privileged users. Access to the different features is split on two privileges: “Read,” to display the section information, and “Write,” which authorizes modifications.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
UserLock’s administrator actions reports also record and track administrator actions.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
AU.L2-3.3.3 Event review: Review and update logged events.
AU.L2-3.3.5 Audit correlation: Correlate audit record review, analysis, and reporting processes for investigation and response to indications of unlawful, unauthorized, suspicious, or unusual activity.
AU.L2-3.3.6 Reduction & reporting: Provide audit record reduction and report generation to support on-demand analysis and reporting.
Both UserLock and FileAudit support compliance with extensive logs and reporting capabilities.
UserLock offers filterable reports on all user access events, including MFA events. Admins can easily review these reports in the UserLock dashboard, and powerful filters make it simple to focus only on the information needed. Reports can be sent via email to relevant parties for ongoing reporting or compliance purposes.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
FileAudit provides a centralized audit log of all file access events by user and also tracks and reports on NTFS permissions. In other words, administrators can access reports that answer who did what, and when, for all of your Windows file servers, files, folders, and data in cloud storage. As with UserLock, all FileAudit reports can be sent via email to relevant parties for ongoing reporting or compliance purposes.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
SI.L2-3.14.7 Identify unauthorized use: Identify unauthorized use of organizational systems.
Both UserLock and FileAudit monitor and record denied accesses.
For example, if a person attempts to log into one of your Active Directory accounts from overseas, but you’ve blocked all logons that originate from outside your organization’s home country, that logon will be denied.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
In the case of FileAudit, if a user tries to access a file they don’t have permissions to view, FileAudit alerts the administrator and records the attempt. You can also set up automated scripts to deny access immediately.
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
By aligning access management and auditing practices with CMMC 2.0 requirements, you can strengthen your security posture while making compliance simpler and more sustainable. With UserLock and FileAudit, you can put essential CMMC controls in place quickly, without adding complexity.